将高分辨率图像分割成大小均匀的图像用于训练,可以提高训练效率,提高模型性能,并提供更大的灵活性。
一、大小均匀图像用于训练优势
内存管理:高分辨率图像通常占用大量内存。通过将它们分割成较小的图像,可以更有效地利用内存,使训练过程更加高效。
并行化:小图像可以在多个处理器或GPU上并行处理,这可以大大提高训练速度。
避免过拟合:通过从大图像中提取出许多小图像,可以增加训练样本的数量,这有助于提高模型的泛化能力,避免过拟合。
学习局部特征:在许多情况下,图像的局部特征(如纹理、形状等)对于任务来说可能是非常重要的。使用小图像可以使模型更专注于这些局部特征。
灵活性:分割后的小图像可以适应各种网络结构,特别是那些设计用于处理固定大小输入的网络。
二、代码
2.1 代码参数修改
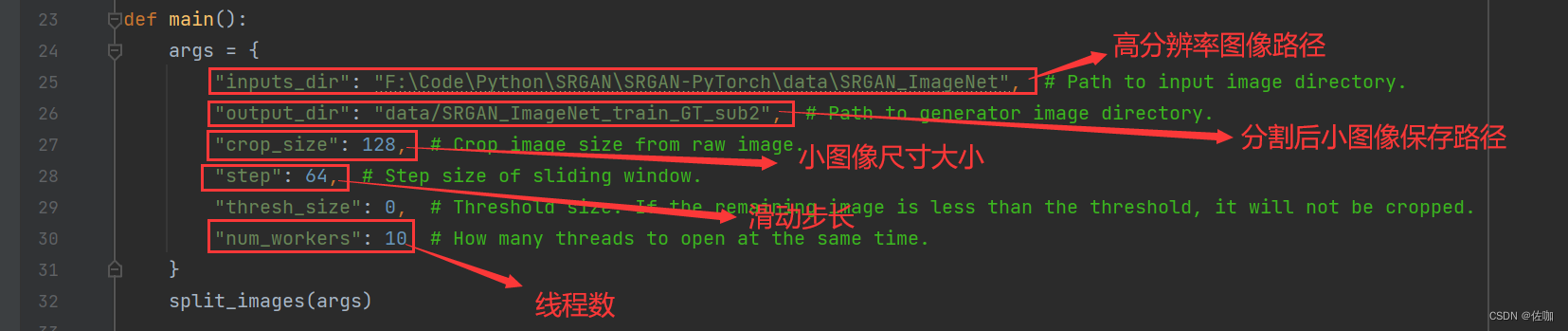
下面是使用代码,根据自己情况修改参数,其中output_dir是裁剪后小图像的保存路径,此路径在代码中设置就行,不用在本地文件夹中提前创建好。
2.2 代码
import multiprocessing
import os
import sys
import cv2
import numpy as np
from tqdm import tqdm
def main():
args = {
"inputs_dir": "F:\Code\Python\SRGAN\SRGAN-PyTorch\data\SRGAN_ImageNet", # Path to input image directory.
"output_dir": "data/SRGAN_ImageNet_train_GT_sub2", # Path to generator image directory.
"crop_size": 128, # Crop image size from raw image.
"step": 64, # Step size of sliding window.
"thresh_size": 0, # Threshold size. If the remaining image is less than the threshold, it will not be cropped.
"num_workers": 10 # How many threads to open at the same time.
}
split_images(args)
def split_images(args: dict):
"""Split the image into multiple small images.
Args:
args (dict): Custom parameter dictionary.
"""
inputs_dir = args["inputs_dir"]
output_dir = args["output_dir"]
num_workers = args["num_workers"]
if not os.path.exists(output_dir):
os.makedirs(output_dir)
print(f"Create {output_dir} successful.")
else:
print(f"{output_dir} already exists.")
sys.exit(1)
# Get all image paths
image_file_paths = os.listdir(inputs_dir)
# Splitting images with multiple threads
progress_bar = tqdm(total=len(image_file_paths), unit="image", desc="Split image")
workers_pool = multiprocessing.Pool(num_workers)
for image_file_path in image_file_paths:
workers_pool.apply_async(worker, args=(image_file_path, args), callback=lambda arg: progress_bar.update(1))
workers_pool.close()
workers_pool.join()
progress_bar.close()
print("Split image successful.")
def worker(image_file_path: str, args: dict):
"""Split the image into multiple small images.
Args:
image_file_path (str): Image file path.
args (dict): Custom parameter dictionary.
"""
inputs_dir = args["inputs_dir"]
output_dir = args["output_dir"]
crop_size = args["crop_size"]
step = args["step"]
thresh_size = args["thresh_size"]
image_name, extension = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(image_file_path))
image = cv2.imread(os.path.join(inputs_dir, image_file_path), cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)
image_height, image_width = image.shape[0:2]
image_height_space = np.arange(0, image_height - crop_size + 1, step)
if image_height - (image_height_space[-1] + crop_size) > thresh_size:
image_height_space = np.append(image_height_space, image_height - crop_size)
image_width_space = np.arange(0, image_width - crop_size + 1, step)
if image_width - (image_width_space[-1] + crop_size) > thresh_size:
image_width_space = np.append(image_width_space, image_width - crop_size)
index = 0
for h in image_height_space:
for w in image_width_space:
index += 1
# Crop
crop_image = image[h: h + crop_size, w:w + crop_size, ...]
crop_image = np.ascontiguousarray(crop_image)
# Save image
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(output_dir, f"{image_name}_{index:04d}{extension}"), crop_image)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
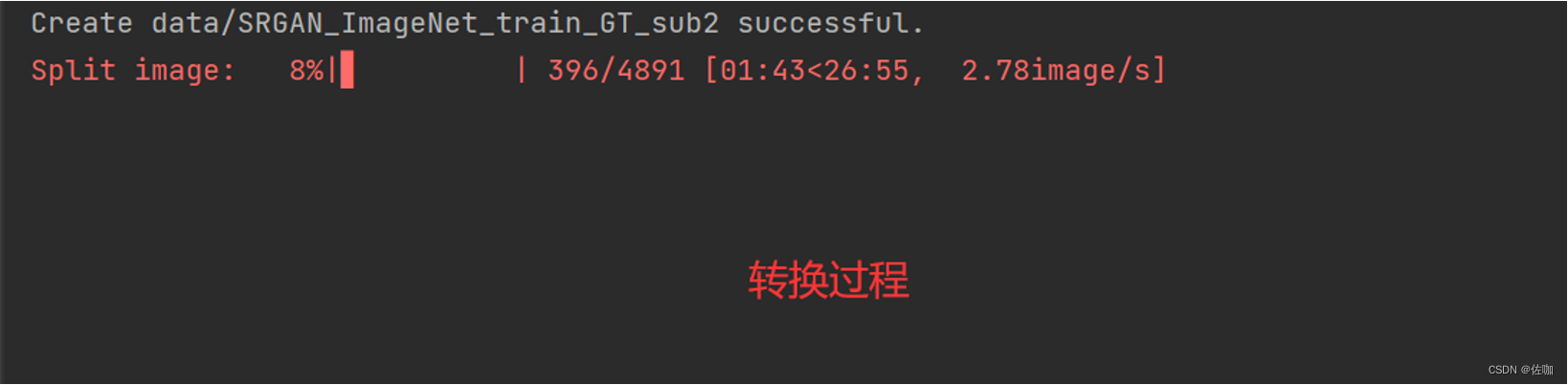
2.3 输出
分割过程如下,高分辨率图像较多时,会等待很久…
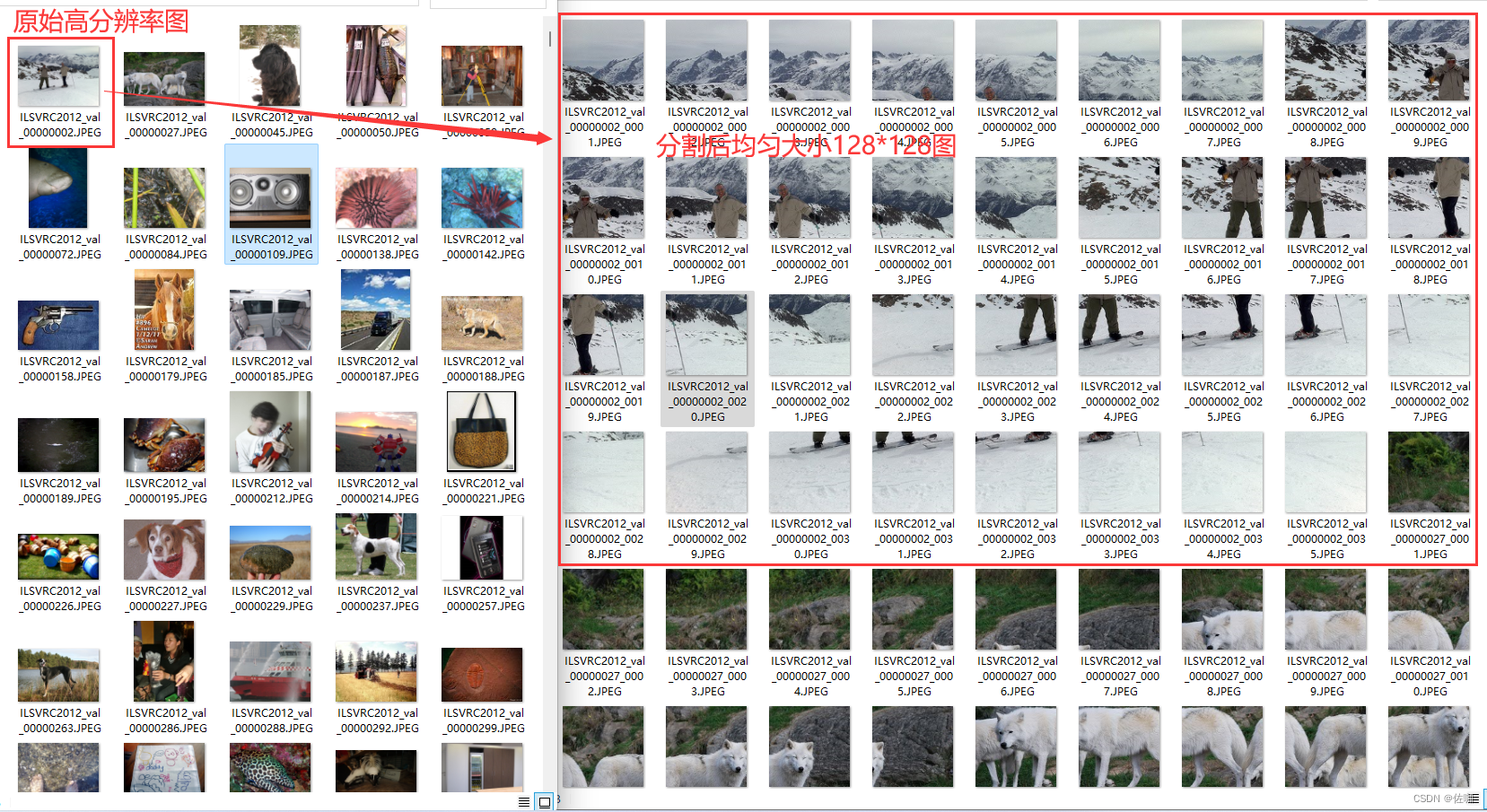
2.4 分割结果
三、总结
以上就是数据集制作,将高分辨率图像分割成大小均匀图像的详细方法,后续还可以再均匀大小图像基础上进一步做数据增强,数据增强方法参考博文:数据增强
感谢您阅读到最后!关注公众号「视觉研坊」,获取干货教程、实战案例、技术解答、行业资讯!