学习TTS遇到的问题2 什么是TCN模型
什么是TCN模型
https://juejin.cn/post/7262269863343079479
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_57726558/article/details/132163074
由下图箭头可知,TCN第一层,每相邻两个单元输出到一个单元,下一层网络间隔一个单元输出到下一层网络,第三层网络间隔2的指数 两个单元输出到下一层网络, 一直继续下去网络的顶层能看到底层所有单元的信息。
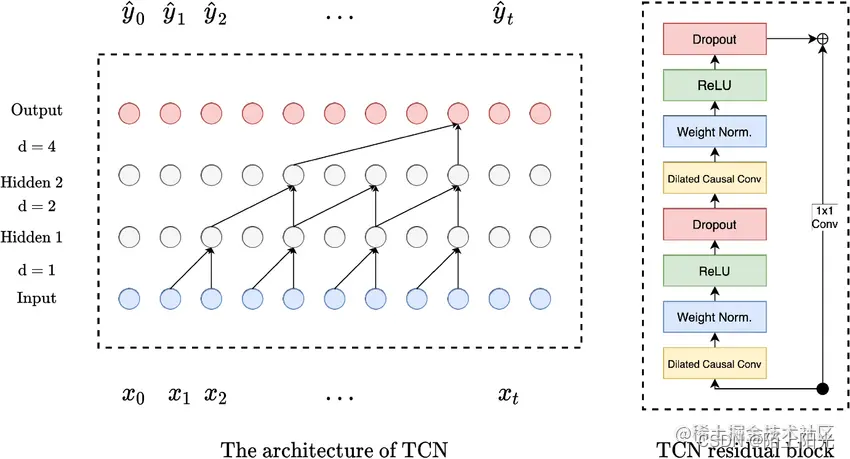
怎么理解 TCN中的 dilation?
dilation=1, 可以看到
2
∗
1
2*1
2∗1的输入单元–信息
dilation=2, 可以看到
2
∗
2
2*2
2∗2的输入单元–信息
dilation=4, 可以看到
2
∗
4
2*4
2∗4的输入单元–信息
dilation=8, 可以看到
2
∗
8
2*8
2∗8的输入单元–信息
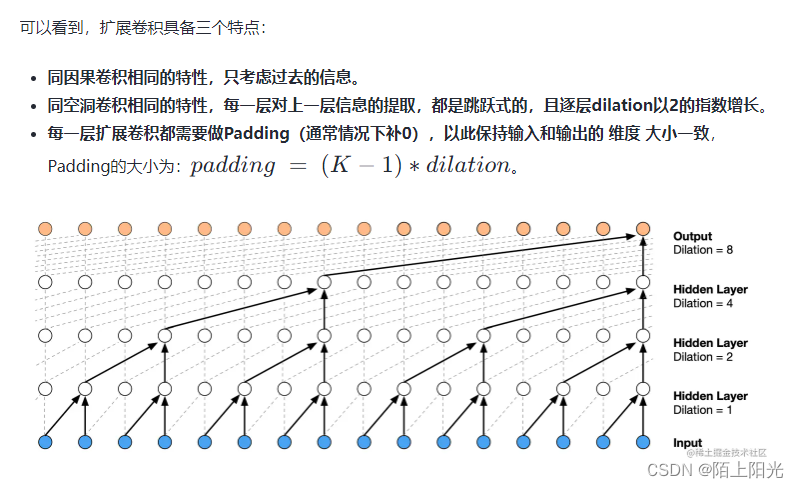
TCN(Temporal Convolutional Network)中的 dilation(膨胀)是用于在卷积操作中扩展感受野的一种技术。它通过在卷积核之间引入空洞来实现。以下是 dilation 的详细解释:
什么是 Dilation
dilation(膨胀)在卷积操作中引入了空洞,使得卷积核的感受野更大,而不需要增加卷积核的大小。具体来说,在应用 dilation 时,卷积核的每两个相邻元素之间会有一些间隔。这些间隔的数量由 dilation rate(膨胀率)决定。
具体例子
假设你有一个1维的卷积核 [w0, w1, w2],dilation rate 为 2,则这个卷积核在应用 dilation 后变为 [w0, 0, w1, 0, w2]。这里的 0 表示引入的空洞。
数学表达
在没有 dilation 的情况下,一个1维卷积操作的输出可以表示为:
y
(
t
)
=
∑
k
=
0
K
−
1
x
(
t
−
k
)
⋅
w
(
k
)
y(t) = \sum_{k=0}^{K-1} x(t-k) \cdot w(k)
y(t)=∑k=0K−1x(t−k)⋅w(k)
其中:
- y ( t ) y(t) y(t) 是输出。
- x ( t ) x(t) x(t) 是输入。
- w ( k ) w(k) w(k) 是卷积核。
- K K K 是卷积核的大小。
当引入 dilation 后,卷积操作的输出变为:
y
(
t
)
=
∑
k
=
0
K
−
1
x
(
t
−
d
⋅
k
)
⋅
w
(
k
)
y(t) = \sum_{k=0}^{K-1} x(t-d \cdot k) \cdot w(k)
y(t)=∑k=0K−1x(t−d⋅k)⋅w(k)
其中
d
d
d 是 dilation rate。这样,卷积核中的每个元素在输入序列中间隔
d
d
d 个元素进行卷积。
作用
- 扩展感受野:dilation 扩展了卷积核的感受野,可以在不增加计算量的情况下捕捉更大范围的上下文信息。
- 保留分辨率:与池化操作不同,dilation 不会丢失数据的分辨率。
- 有效处理长序列:对于时间序列或序列数据,dilation 有助于捕捉远距离的依赖关系。
例子
假设有一个长度为 10 的输入序列 x = [x0, x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8, x9],一个卷积核 w = [w0, w1, w2],dilation rate 为 2。卷积操作的过程如下:
y(t) = x(t) * w0 + x(t-2) * w1 + x(t-4) * w2
这个操作会在卷积核的每个元素之间跳过 2 个输入元素。
代码示例
以下是 PyTorch 中实现 TCN 的一个简单示例,展示了如何使用 dilation:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class TCN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, output_size, num_channels, kernel_size=2, dropout=0.2):
super(TCN, self).__init__()
layers = []
num_levels = len(num_channels)
for i in range(num_levels):
dilation_size = 2 ** i
in_channels = input_size if i == 0 else num_channels[i-1]
out_channels = num_channels[i]
layers += [nn.Conv1d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=(kernel_size-1)*dilation_size, dilation=dilation_size),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(dropout)]
self.network = nn.Sequential(*layers)
self.linear = nn.Linear(num_channels[-1], output_size)
def forward(self, x):
y1 = self.network(x)
y2 = self.linear(y1[:, :, -1])
return y2
# Example usage
tcn = TCN(input_size=1, output_size=10, num_channels=[25, 50])
input_data = torch.randn(32, 1, 100) # (batch_size, num_channels, sequence_length)
output = tcn(input_data)
print(output.shape) # (batch_size, output_size)
在这个示例中,每一层卷积都会以2的指数倍方式增加 dilation,从而在每一层中逐步扩展感受野。