String类的创建
使用常量串构造
String str1 = "hello";
就是直接赋值(赋予一个常量字符串)的意思
new String 对象
String str2 = new String("world");
使用字符数组进行构造
下面是String自带的构造方法,能把字符数组转化为String类
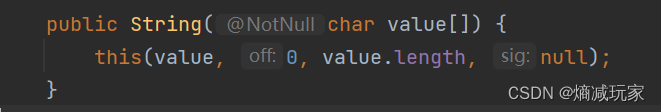
char[] arr = {'a','b','c','d'};
String str3 = new String(arr);
String的JVM分布
String本质上是一个类,我们可以从下面得知String类内部是包含几个成员变量的:

value这个成员变量就是用来存放字符的,其他的成员变量还有coder、hash、hashIsZero
所以如果我们创建一个String类的话,JVM的分布图应该为如下图所示,这里之讨论value成员变量!!!
String str1 = "hello";
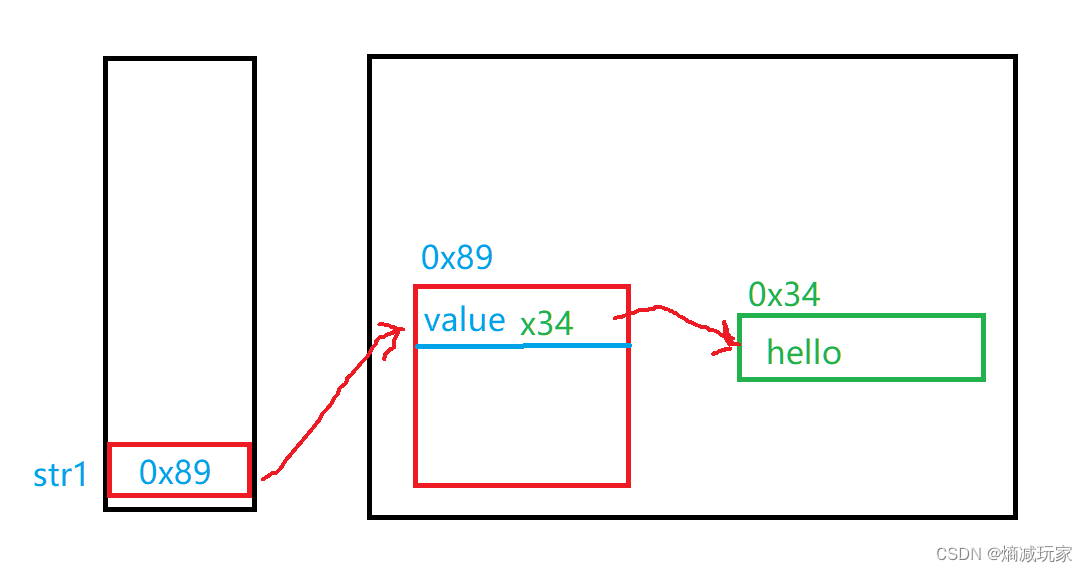
String包含的字符串是没有以 \0 结尾的!!!
String类内部的方法使用介绍
String 和 数组的长度求取区别
String求字符串长度使用的是length 方法,而且这不是一个静态方法,是需要通过具体的对象去调用才能使用的方法
数组长度的求取使用的直接.length就可以了
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("hello");
int length = str.length();
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
int length2 = arr.length;
}
String对象的比较
==
如果使用 == 比较的是基本数据类型的话就是比较他们的值是否相等,如果比较的是引用类型变量的话,那比较的就是他们所引用的对象是否相同。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "hello";
String str2 = "world";
String str3 = str1;
System.out.println(str1 == str2);
System.out.println(str1 == str3);
System.out.println(str2 == str3);
}

public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("hello");
String str2 = new String("hello");
String str3 = str1;
System.out.println(str1 == str2);
System.out.println(str1 == str3);
System.out.println(str2 == str3);
}

equals
equals 方法在之前文章有提过,现在简单提一下,equals 方法是Object类自带的,如果使用Object类自带的equals方法就还是跟上面我们提到的 == 的使用规则是一样的(也就是根据地址来进行判断),如果需要根据内容进行判断的话,就必须重写equals方法,在String类内部是重写过equals的,equals 的放回值是boolean类型,如下图:
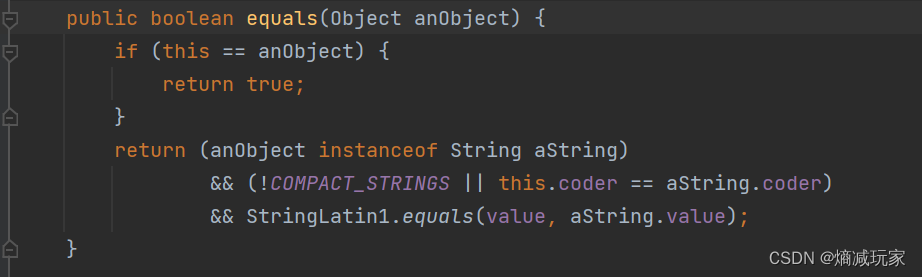
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("hello");
String str2 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));
}

comparaTo
String类是实现了Comparable 接口的,所以我们可以使用comparaTo方法来比较字符串的内容,comparaTo的放回值是整型数字。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("hello");
String str2 = new String("hello");
String str3 = new String("HELLO");
String str4 = new String("world");
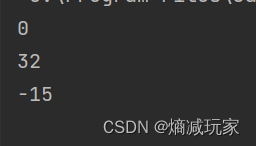
System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str2));
System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str3));
System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str4));
}
compareToIgnoreCase
忽略字母大小写来比较
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("hello");
String str2 = new String("hello");
String str3 = new String("HELLO");
String str4 = new String("HellO");
String str5 = new String("Hello汉字world");
String str6 = new String("hello汉字WORLD");
System.out.println(str1.compareToIgnoreCase(str2));
System.out.println(str1.compareToIgnoreCase(str3));
System.out.println(str1.compareToIgnoreCase(str4));
System.out.println(str5.compareToIgnoreCase(str6));
}

如果你的String包含汉字的话,也是正常比较的,comparaToIgnoreCase只是忽略字母的大小写
字符串查找
charAt
返回下标所对应的字符
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello";
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
System.out.print(ch + " ");
}
}
indexOf
indexOf是寻找第一次出现某个字符或者字符串所在的位置,并返回其下标。
这个方法有很多重载的方法,我们可以不同的需求来使用即可
indexOf (int ch)
寻找某个字符第一次出现的位置
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("hello");
int index = str.indexOf('l');
System.out.println(index);
}
indexOf (int ch, int fromIndex)
从fromIndex这个位置开始寻找
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("hello");
int index = str.indexOf('l',3);
System.out.println(index);
}
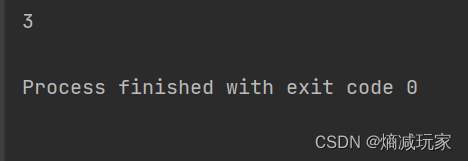
indexOf (String str)
这个是寻找某个字符串第一次出现的位置
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("hello");
int index = str.indexOf("ell");
System.out.println(index);
}
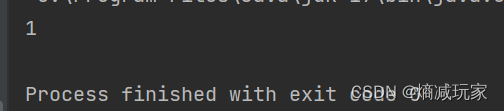
indexOf (String str, int fromIndex)
从fromIndex开始寻找某个字符串第一次出现的位置
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("hello");
int index = str.indexOf("ll",3);
System.out.println(index);
}
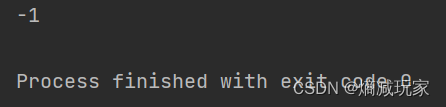
lastIndexOf
从后面开始寻找
lastIndexOf (int ch)
从最后面的字符开始向前寻找第一个字符出现的位置
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("hello");
int index = str.lastIndexOf('l');
System.out.println(index);
}
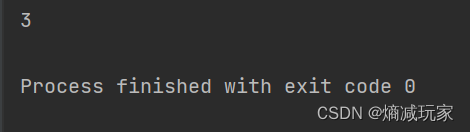
lastIndexOf (int ch,int fromIndex)
从某个位置开始向前寻找某个字符第一次出现的位置
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("hello");
int index = str.lastIndexOf('l',2);
System.out.println(index);
}
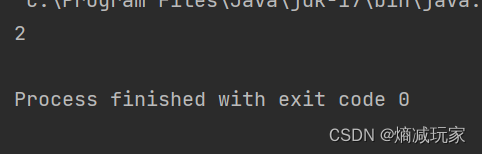
lastIndexOf (String str)
从最后面开始向前寻找字符串第一次出现的位置
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("hello");
int index = str.lastIndexOf("ll");
System.out.println(index);
}
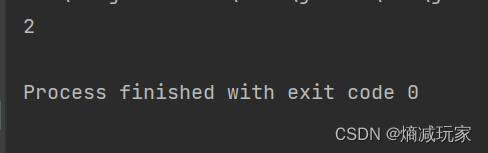
lastIndexOf (String str, int fromIndex)
从fromIndex开始向前寻找字符串第一次出现的位置
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("hello");
int index = str.lastIndexOf("ll",2);
System.out.println(index);
}
转化
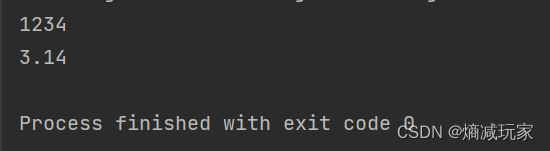
valueOf(数值) —— 数值和字符串转化
valueOf 是静态方法,直接通过 String 调用即可,这个方法可以将数值转变为字符串。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = String.valueOf(1234);
String str2 = String.valueOf(3.14);
System.out.println(str1);
System.out.println(str2);
}
大小写转化
toUpperCase()
这个方法是将字符串所有的字符转变为大写
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "hello";
String str2 = "WorLD";
System.out.println(str1.toUpperCase());
System.out.println(str2.toUpperCase());
}
toLowerCase
字符串转小写
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "heLLO";
String str2 = "WorLD";
System.out.println(str1.toLowerCase());
System.out.println(str2.toLowerCase());
}
字符串转数组 —— toCharArray()
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello";
char[] arr = str.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
格式化
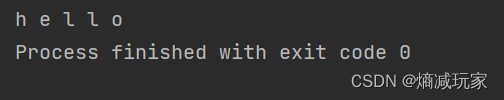
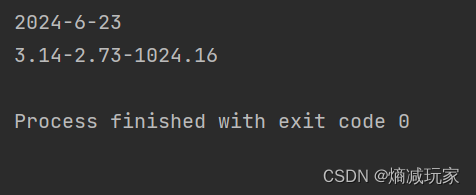
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = String.format("%d-%d-%d",2024,6,23);
System.out.println(str);
String str2 = String.format("%.2f-%.2f-%.2f",3.14,2.73,1024.16);
System.out.println(str2);
}
字符串替换
replace(char oldChar, char newChar)
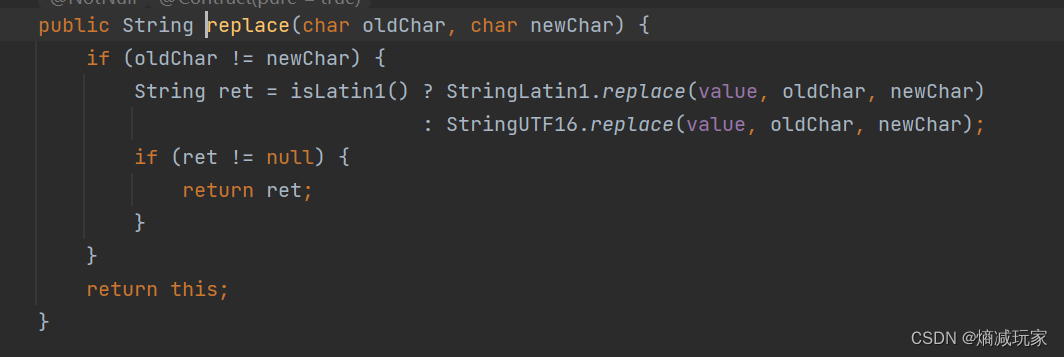
将所有的旧字符替换成新字符
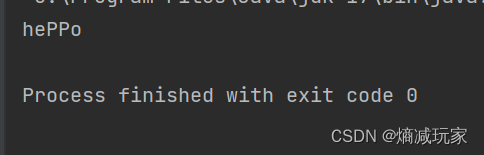
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "hello";
String str2 = str1.replace('l','P');
System.out.println(str2);
}
replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement)
将所有的目标字符串替换成新的字符串
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "helloQlloQllo";
String str2 = str1.replace("llo","AA");
System.out.println(str2);
}
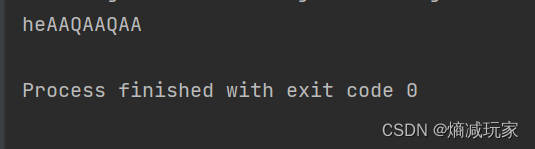
replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement)
将一个字符或者字符串替换为新字符或者新字符串
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "hellQllo";
String str2 = str1.replaceFirst("l","P");
System.out.println(str2);
String str3 = str1.replaceFirst("ll","SS");
System.out.println(str3);
}
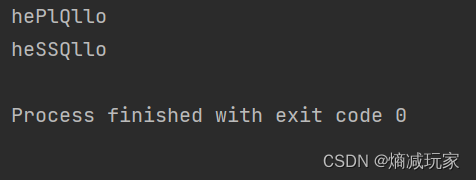
replaceAll(String regex, String replacement)
将所有的目标字符或者目标字符串替换为新字符或者新字符串
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "hellQllo";
String str2 = str1.replaceAll("l","P");
System.out.println(str2);
String str3 = str1.replaceAll("ll","SS");
System.out.println(str3);
}
字符串拆分
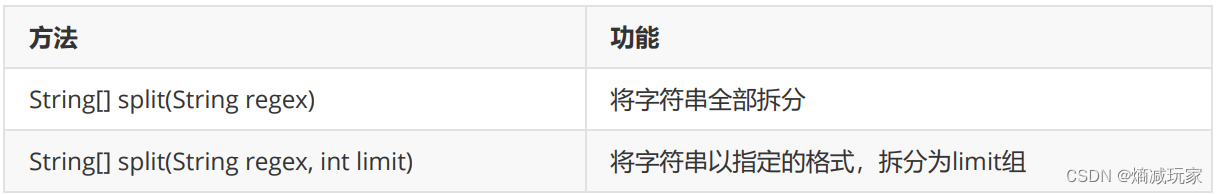
split(String regex)
将字符串以某个标准进行拆分
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "hello world";
String[] strings = str1.split("l");
for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) {
System.out.println(strings[i]);
}
System.out.println("===========================");
String[] strings2 = str1.split("ll");
for (int i = 0; i < strings2.length; i++) {
System.out.println(strings2[i]);
}
}
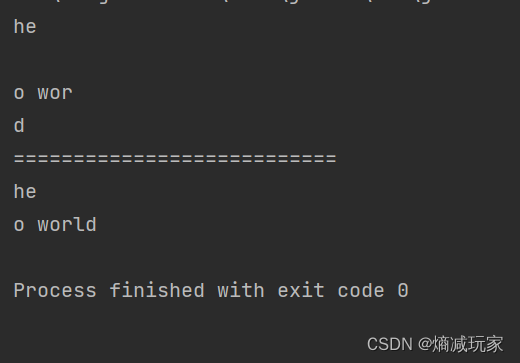
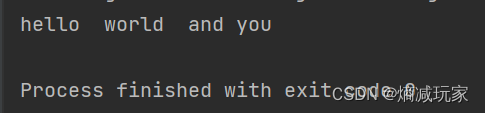
split(String regex, int limit)
将字符串以指定的格式,拆分成limit个组
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello world and you";
String[] str2 = str.split(" ",3);
for (int i = 0; i < str2.length; i++) {
System.out.println(str2[i]);
}
}
特殊符号的分割
- 字符"|“, “*” ,”+"都得加上转义字符,前面加上 “\” .
- 如果是 " \ " ,那么就得写成 “\\” .
- 如果一个字符串中有多个分隔符,可以用"|"作为连字符.
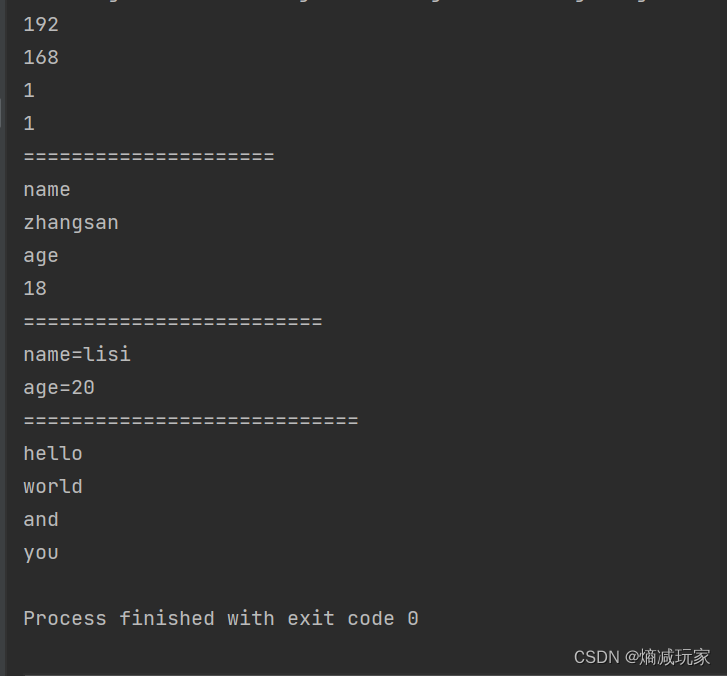
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "192.168.1.1";
String[] str2 = str.split("\\.");
for (int i = 0; i < str2.length; i++) {
System.out.println(str2[i]);
}
System.out.println("=====================");
String str3 = "name=zhangsan&age=18" ;
String[] result = str3.split("=|&") ;
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
System.out.println(result[i]);
}
System.out.println("=========================");
String str4 = "name=lisi+age=20";
String[] strings3 = str4.split("\\+");
for (int i = 0; i < strings3.length; i++) {
System.out.println(strings3[i]);
}
System.out.println("============================");
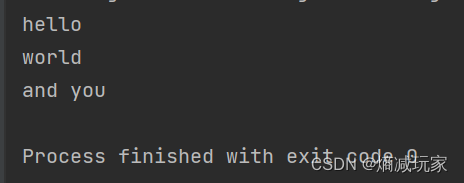
String str5 = "hello\\world\\and\\you";
String[] result2 = str5.split("\\\\");
for (int i = 0; i < result2.length; i++) {
System.out.println(result2[i]);
}
}
字符串的截取
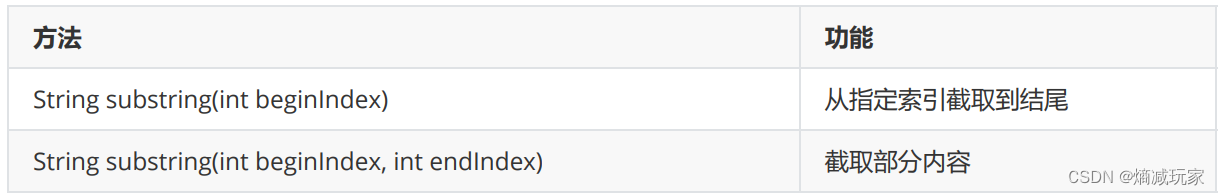
subString(int beginIndex)
从beginIndex开始截取字符串
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello world";
String str2 = str.substring(3);
System.out.println(str2);
}
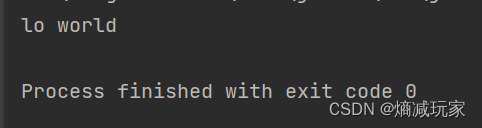
subString(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
从beginIndex 到 endIndex 的范围截取对应的字符串,这里的范围是左闭右开
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello world";
String str2 = str.substring(3,7);
System.out.println(str2);
}
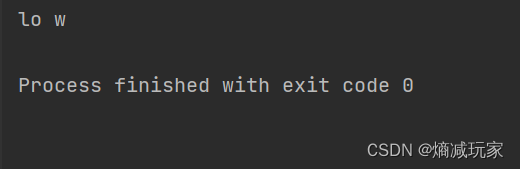
trim()
去掉字符串中的左右空格,保留中间空格
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = " hello world and you ";
String str2 = str.trim();
System.out.println(str2);
}
String 类 的内容的不可变性
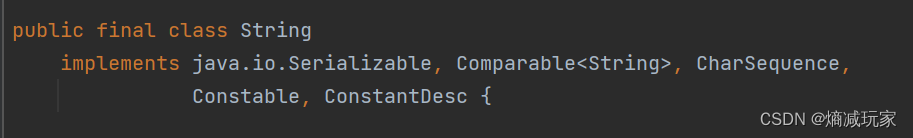
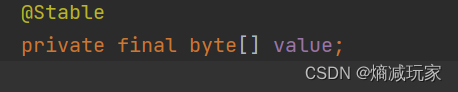
String 类 的 内容 一旦创建之后,就不能被修改,我们从上图可以看出value 是被private 修饰的,因此value值一旦创建好就只能在String类内部使用,外部是无法改变value的值的,因此String类的内容具有不可变性。
这里再拓展一下final关键字,被final修饰的类是密封类也就是不能被继承的,被final修饰的引用变量是不能改变其指向的对象,但是可以改变这个引用变量所指向的对象的数值,所以final不是String类的内容具有不可变性的原因。
StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 介绍
字符串的修改
如果你要进行字符串的修改的时候,建议使用StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder ,因为直接使用String类进行修改的话,会创建很多临时对象,导致效率低下。
System.currentTimeMillis() 是记录当前系统的时间的,我们可以通过下面代码来感受一个使用String,StringBuffer和StringBuilder这三个不同的工具来拼接字符串需要的时间消耗。
public static void main(String[] args) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String s = "";
for(int i = 0; i < 10000; ++i){
s += i;
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
StringBuffer sbf = new StringBuffer("");
for(int i = 0; i < 10000; ++i){
sbf.append(i);
}
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
StringBuilder sbd = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = 0; i < 10000; ++i){
sbd.append(i);
}
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
}
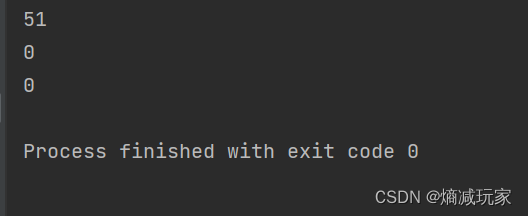
从上面我们可以得知String的效率很低,所以如果要修改字符串的话,建议使用StringBuffer和StringBuilder来进行操作。
方法
由于StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 的方法命名和使用是一样的,所以这里只列举出StringBuffer的方法…
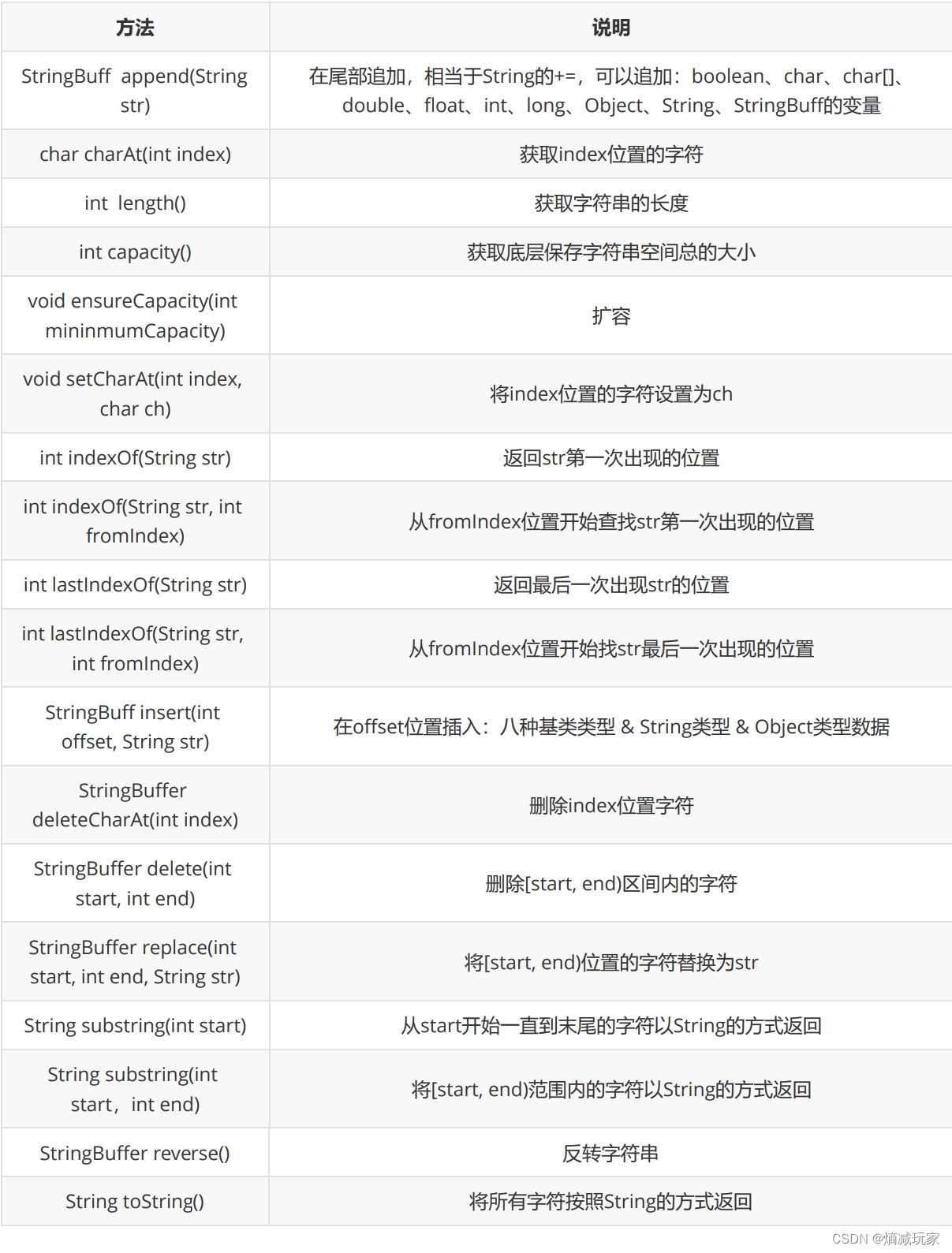
这里要注意如果使用StringBuffer或者StringBuilder来修改字符串的时候,它们的返回值是StringBuffer 或者 StringBuilder ,如果需要转换为String类,那就要使用toString() 方法。
String变为StringBuilder: 利用StringBuilder的构造方法或append()方法
区别
StringBuffer采用同步处理,属于线程安全操作;而StringBuilder未采用同步处理,属于线程不安全操作。
StringBuffer里的方法有synchronized修饰,这个单词是同步的,同步化的意思,也就是说StringBuffer采用的是同步处理,使用在多线程上,因此StringBuffer可以保护线程安全。
StringBuilder的方法是没有进行同步处理的,也就是意味着它使用在单线程的场景里。
所以如果需要频繁地修改字符串的话,使用StringBuffer或者StringBuilder,如果使用在多线程里,则使用StringBuffer;如果使用在单线程里,则使用StringBuilder。
不建议不分场景地使用StringBuffer,因为StringBuffer会频繁地开锁和解锁,如果是使用在单线程里的话,就会造成资源的浪费!!!