1. 链表数据结构
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
2. 链表的删除
2.1 移除链表元素
- 力扣:https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
if(head == NULL) return NULL;
ListNode *dummy= new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
ListNode *pre = dummy;
ListNode *cur = head;
while(cur){
if(cur->val == val){
ListNode *tmp = cur->next;
pre->next = tmp;
delete(cur);
cur = tmp;
}
else{
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return dummy->next;
}
2.2 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
- 力扣:https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/description/
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode* slow = dummyHead;
ListNode* fast = dummyHead;
while(n-- && fast) {
fast = fast->next;
}
fast = fast->next; // fast再提前走一步,因为需要让slow指向删除节点的上一个节点
while (fast) {
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
slow->next = slow->next->next;
ListNode *tmp = slow->next;
slow->next = tmp->next;
delete tmp;
return dummyHead->next;
}
3. 链表的移动
3.1 反转链表
- 力扣:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL) return NULL;
if(head->next == NULL) return head;
ListNode *pre = NULL;
ListNode *cur = head;
while(cur){
ListNode *tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
return pre;
}
3.2 两两交换链表节点
- 力扣:https://leetcode.cn/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/description/
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL) return NULL;
if(head->next == NULL) return head;
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
ListNode *pre = dummy;
ListNode *cur = head;
while(cur && cur->next){
ListNode *tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = tmp->next;
tmp->next = cur;
pre->next = tmp;
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
return dummy->next;
}
3.3 反转链表的一部分
- 力扣:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/description/
ListNode *reverseBetween(ListNode *head, int left, int right) {
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
ListNode *pre = dummy;
// 第 1 步:从虚拟头节点走 left - 1 步,来到 left 节点的前一个节点
for (int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++) {
pre = pre->next;
}
// 第 2 步:从 pre 再走 right - left + 1 步,来到 right 节点
ListNode *rightNode = pre;
for (int i = 0; i < right - left + 1; i++) {
rightNode = rightNode->next;
}
// 第 3 步:切断出一个子链表(截取链表)
ListNode *leftNode = pre->next;
ListNode *curr = rightNode->next;
pre->next = nullptr;
rightNode->next = nullptr;
// 第 4 步:同上一题,反转链表的子区间
reverseLinkedList(leftNode);
// 第 5 步:接回到原来的链表中
pre->next = rightNode;
leftNode->next = curr;
return dummy->next;
}
3.4 K个一组反转链表
- 力扣:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/description/
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
ListNode *left = head; //每组的第一个
ListNode *right = dummy; //每组的第k个,初始为left的前一个节点
ListNode *beforePre = dummy; //反转前本组的前驱
while(left){
for(int i = 0; i < k; ++i){
if(right->next) right = right->next;
else return dummy->next; //不足k个结点,反转结束
}
ListNode *beforeNext = right->next; //即为下一组的left
ListNode *pre = nullptr;
ListNode *cur = left;
while(pre != right){
ListNode *tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
beforePre->next = right;
left->next = beforeNext;
right = left;
beforePre = left;
left = beforeNext;
}
return dummy->next;
}
3.5 旋转链表
- 力扣:https://leetcode.cn/problems/rotate-list/description/
3.6 分隔链表
- 力扣:https://leetcode.cn/problems/partition-list/description/
4. 链表的相交
4.1 链表相交
- 力扣:https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci/description/
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
ListNode* curA = headA;
ListNode* curB = headB;
int lenA = 0, lenB = 0;
while (curA) {
lenA++;
curA = curA->next;
}
while (curB) {
lenB++;
curB = curB->next;
}
curA = headA;
curB = headB;
int gap = 0;
if (lenB > lenA) {
gap = lenB -lenA;
while(gap--) curB = curB->next;
}
else{
gap = lenA - lenB;
while (gap--) curA = curA->next;
}
while (curA) {
if (curA == curB) return curA;
curA = curA->next;
curB = curB->next;
}
return NULL;
}
4.2 合并链表
- 力扣:https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/description/
4.3 环形链表
- 力扣:https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while(fast && fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast) {
ListNode* index1 = fast;
ListNode* index2 = head;
while (index1 != index2) {
index1 = index1->next;
index2 = index2->next;
}
return index2; // 返回环的入口
}
}
return NULL;
}
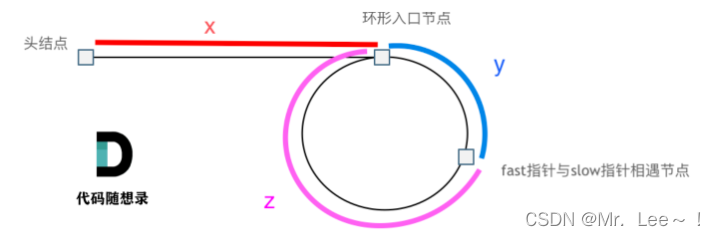
- 判断环入口的方法:
- 相遇时,slow指针走过的节点数为:
x + y, fast指针走过的节点数:x + y + n (y + z)
- 因为fast指针是一步走两个节点,slow指针一步走一个节点, 所以
(x + y) * 2 = x + y + n (y + z),得到 x = n (y + z) - y
- 整理公式之后为如下公式:
x = (n - 1) (y + z) + z
- 当
n = 1 时,得到 x = z,这就意味着:从头结点出发一个指针,从相遇节点 也出发一个指针,这两个指针每次只走一个节点, 那么当这两个指针相遇的时候就是 环形入口的节点
5. 其他
5.1 LRU缓存(链表常考题)
- 力扣:https://leetcode.cn/problems/lru-cache/description/
